
ZATCA E-Invoicing Case Study
The ZATCA Phase 2 Integration is a key milestone in Saudi Arabia’s ongoing digital tax reforms. The initiative seeks to streamline the invoicing process, ensuring compliance with the ZATCA e-invoicing system, which started in December 2021. Saudi Arabia's e-invoicing initiative aligns with Vision 2030's digital transformation goals. This case study highlights how businesses in the Kingdom transitioned to a compliant, transparent, and efficient invoicing system, setting an example for neighboring regions.
The ZATCA Phase 2 Integration is a critical component of Saudi Arabia’s efforts to modernize its tax system, driving efficiency and compliance through digital invoicing solutions. The Zakat, Tax, and Customs Authority (ZATCA) has embarked on a transformative journey to digitalize the tax system, making it more transparent, efficient, and compliant with global standards. The ZATCA e-invoicing initiative is an essential step in this digital transformation. This initiative aims to streamline business operations, improve the collection of taxes, and ensure that tax evasion becomes more difficult through advanced technological frameworks.
The backbone of ZATCA’s e-invoicing system includes robust cryptographic algorithms and advanced integration mechanisms. Businesses use cryptographic stamps, which ensure invoice authenticity, and secure APIs for real-time invoice submission to ZATCA’s Fatoora platform. The system is designed to be future-proof and adaptive to evolving compliance requirements. The ZATCA e-invoicing initiative enforces all businesses, including restaurants, retailers, and service providers, to generate and report invoices electronically. By enforcing the mandatory transition from manual and semi-digital invoicing to fully digital systems, ZATCA ensures that Saudi Arabia's businesses are aligned with the global shift towards more stringent tax compliance and transparency.
This system is powered by advanced technologies such as the Fatoora Platform, which facilitates the seamless real-time reporting of invoices to ZATCA. Since the launch of ZATCA e-invoicing, businesses have reported a significant reduction in manual errors, faster VAT returns processing, and an improved ability to detect discrepancies. Additionally, consumer confidence has increased due to the transparency enabled by QR code-based validation on invoices. The e-invoicing system not only guarantees tax compliance but also makes it easier for businesses to stay on top of their tax obligations without manual intervention, reducing errors and improving efficiency.
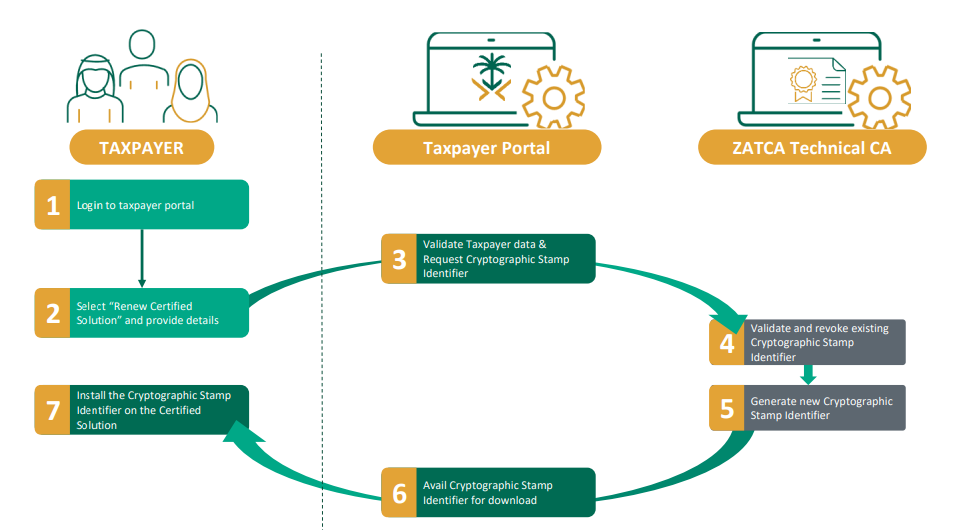
Phases of ZATCA E-Invoicing
Phase 1: Generation Phase (December 2021) ▼
The first phase of ZATCA's e-invoicing implementation, which began in December 2021, focused on the generation of electronic invoices. During this phase, businesses were required to transition from traditional paper-based or semi-digital invoicing systems to fully digital formats. This transition aimed to ensure that all invoices were compliant with the basic standards set by ZATCA.
Generation of Electronic Invoices phase, where Persons subject to the E-Invoicing Regulations must generate Electronic Invoices and associated Electronic Notes in accordance with the clauses set forth under the Resolution on the Controls, Requirements, Technical Specifications and Procedural Rules and any subsequent resolutions. However, the first phase did not yet require direct integration with the ZATCA platform. Businesses were expected to ensure the correct storage and generation of invoices that included all the necessary details, such as the VAT amount and business information, in a digital format. The key goal of this phase was to get businesses accustomed to the new invoicing standards.
- Digital generation of invoices with all essential fields.
- Mandatory electronic storage of invoices for easy retrieval and audit purposes.
- Preparation for future integration with ZATCA systems.
Key Features:
The Generation Phase marked the foundational step in Saudi Arabia’s e-invoicing journey. Businesses were required to transition to generating electronic invoices and credit/debit notes that adhered to ZATCA standards.
-
Structured Format:
- E-invoices had to be generated in a structured electronic format (XML or PDF/A-3 with embedded XML). This excluded scanned paper invoices from compliance.
- Inclusion of mandatory fields such as VAT amount, seller information, and invoice reference number. -
Secure Archiving:
- Businesses were required to electronically store invoices in a manner that ensured authenticity, integrity, and readability for ZATCA audits.
- Data hashing was introduced to prevent tampering. -
Simplified E-Invoices for B2C:
- Simplified invoices were required for point-of-sale transactions. These included a QR code to enable easy verification by consumers.
Implementation:
-
Transition to Digital Solutions:
- Businesses adopted electronic invoicing solutions compliant with ZATCA guidelines.
- These solutions were required to generate invoices in formats such as XML or PDF/A-3, ensuring compatibility with future integration phases.
- Vendor-provided tools and certified systems were key to enabling smooth transitions. -
Adherence to Compliance Standards:
- Each invoice was required to include mandatory fields like VAT amount, seller details, and invoice reference number.
- Proper storage protocols ensured data could be retrieved for audits or disputes. -
Focus on Education and Training:
- ZATCA provided educational materials and webinars to help businesses understand the requirements.
- Businesses conducted internal training to familiarize staff with new systems and processes. -
Testing and System Optimization:
- Pilot testing of systems ensured invoice generation aligned with ZATCA’s standards before full implementation.
- Businesses worked with solution providers to troubleshoot any issues during the early adoption phase. -
Compliance without Integration:
- Although there was no real-time connection to ZATCA, businesses were required to maintain system readiness for the integration phase.
- Continuous monitoring and manual reporting practices were adopted for maintaining accuracy in operations.
Illustrative diagrams for Generation Phase
E-Invoicing Solution Requirement for Phase 1 (Generation Phase)
Requirements for generating E-Invoice and Simplified E-Invoice starting from 4 December 2021
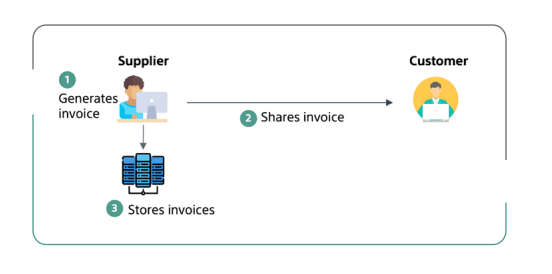
Illustrative diagram for B2B E-Invoice Generation
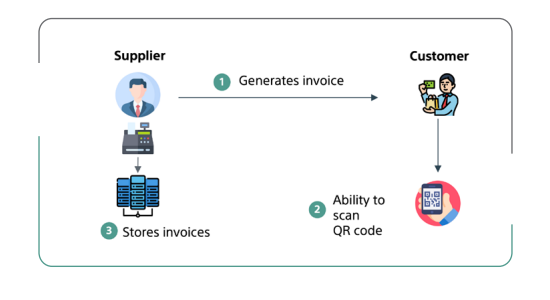
Illustrative diagram for B2C Simplified E-Invoice Generation
Key Components:
- Invoice Generation: Invoices must be generated electronically.
- Invoice Fields: Include non-integration-specific fields.
- Invoice Storage: Invoices stored as per VAT regulations.
- UUID: Unique identifier for traceability.
- QR Code: For instant verification in B2C transactions.
- Internet Connectivity: Required for integration.
Phase 2: ZATCA Phase 2 Integration Phase (January 2023 Onwards) ▼
The second phase, which was implemented in January 2023, marked a significant leap in the digital transformation of Saudi Arabia's tax system, where Persons subject to the E-Invoicing Regulations must integrate their systems with the Authority׳s system in accordance with the clauses set forth under the Resolution on the Controls, Requirements, Technical Specifications and Procedural Rules and any subsequent resolutions. The integration phase will be implemented in phases and will be mandated to Persons subject to the E-Invoicing Regulations based on a certain set of criteria determined by the Authority The target groups will be informed of the integration procedures with the authority׳s systems at least six months before the date set for integration with the target group or groups. This phase made it mandatory for businesses to integrate their invoicing systems with ZATCA’s Fatoora platform. This real-time integration was a crucial step to ensure seamless tax reporting and compliance.
The ZATCA Phase 2 Integration is divided into two main components: B2B (Business-to-Business) and B2C (Business-to-Consumer). Each component focuses on different aspects of the e-invoicing system to address the varying needs of businesses and consumers.
- Real-time reporting for both B2B (Business-to-Business) and B2C (Business-to-Consumer) transactions.
- UUID (Universally Unique Identifier): Ensures invoice traceability.
- Enhanced requirements for restaurants and other sectors.
B2B (Business-to-Business)
The B2B aspect of Phase 2 requires businesses to generate detailed invoices that are automatically transmitted to ZATCA’s platform for real-time reporting. These invoices must include detailed information such as the buyer's VAT number, invoice total, and tax breakdown. This ensures full compliance with ZATCA’s regulations and enables businesses to claim tax credits for transactions with other businesses.
- Invoices must include detailed information such as the buyer's VAT number, invoice total, and tax breakdown.
- Real-time reporting of invoices to ZATCA for verification and tax credit validation.
- Each invoice is assigned a unique identifier (UUID), ensuring traceability and accountability.
- Automatic updates and compliance with ZATCA Phase 2 Integration evolving tax regulations.
B2C (Business-to-Consumer)
The B2C integration focuses on simplifying the invoicing process for consumer transactions. This involves generating simplified invoices that include a QR code. This QR code can be scanned by consumers, allowing them to instantly validate the authenticity of the invoice and confirm that it complies with ZATCA’s regulations. This phase improves consumer trust and ensures that tax collection is accurate and transparent for both businesses and their customers.
- Invoices are simplified with QR codes for easier consumer validation.
- The QR code enables instant verification by consumers, boosting transparency and trust.
- This is particularly important in sectors like retail, restaurants, and other consumer-facing industries.
- Ensures compliance with tax regulations while making the process more user-friendly for consumers.
Key Features:
The Integration Phase represented a leap towards real-time compliance, focusing on seamless connectivity between business systems and ZATCA's platform.
-
Real-Time Invoice Submission:
- Businesses integrated their systems with the Fatoora Platform to report invoices instantly.
- Two modes of compliance emerged:- Clearance: Standard invoices (B2B) required pre-approval from ZATCA before being issued.
- Reporting: Simplified invoices (B2C) had to be reported within 24 hours.
-
Cryptographic Stamping:
- A digital cryptographic stamp was applied to invoices, ensuring their authenticity and integrity.
- Cryptographic algorithms (ECDSA) and hash functions (SHA-256) were mandated for invoice signing. -
Enhanced QR Code Requirements:
- QR codes now encoded additional information, such as a hash of the invoice and the cryptographic stamp, allowing consumers to validate invoice authenticity via ZATCA's portal.
-
Distinction Between B2B and B2C Transactions:
- B2B Transactions: Invoices included buyer VAT details, transaction breakdowns, and UUIDs for traceability.
- B2C Transactions: Simplified invoices enhanced consumer transparency through QR-coded validation.
Implementation:
-
System Integration with ZATCA:
- Businesses integrated their e-invoicing systems directly with the Fatoora Platform, enabling real-time reporting and clearance of invoices.
- This integration required advanced APIs, secure transmission protocols, and compatibility with ZATCA’s centralized e-invoicing platform. -
Adopting Advanced Security Measures:
- Cryptographic stamps were mandated for all invoices, ensuring their authenticity and integrity.
- Secure connections, data encryption, and regular updates to cryptographic algorithms were implemented to safeguard data transmissions. -
Enhanced Functional Capabilities:
- Businesses upgraded their systems to handle high-frequency reporting of B2C invoices within 24 hours.
- Detailed audit trails, invoice numbering sequences, and compliance monitoring dashboards were incorporated. -
Sector-Specific Adjustments:
- Retailers, restaurants, and other high-volume businesses adopted POS systems that generated QR-coded invoices in real-time.
- B2B entities focused on accuracy in VAT details, ensuring invoices included buyer VAT numbers for seamless tax credits. -
Compliance Audits and Reporting:
- ZATCA conducted audits to verify adherence to the integration phase requirements.
- Non-compliant businesses were guided through corrective measures, and penalties were enforced for persistent non-compliance. -
Consumer Empowerment:
- QR codes on invoices allowed consumers to validate authenticity and ensure proper VAT collection.
- This enhanced consumer trust in transactions while reducing tax evasion risks.
Illustrative diagrams for Integration Phase
E-Invoicing Solution Requirement for Phase 2 (Integration Phase)
Requirements for real-time integration starting from January 2023

Illustrative diagram for B2B Integration Phase - Invoice Clearance and Reporting
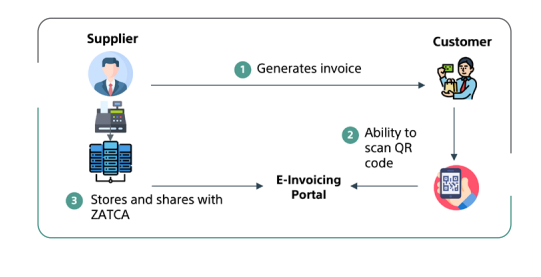
Illustrative diagram for B2C Integration Phase - Instant Consumer Reporting
Key Components:
- Clearance Model: Invoices are cleared in real-time with validation by the Authority.
- Reporting Model: Invoices must be reported to ZATCA within 24 hours of generation.
- Cryptographic Stamps: Ensure invoice authenticity and integrity.
- API Integration: Invoices shared in XML format via ZATCA's API.
- UUID: Unique traceability identifier for all invoices.
- Internet Connectivity: Required to ensure seamless real-time integration.
- Consumer Verification: QR codes for B2C transactions enable instant verification.
Solutions We Provide
DigiPos: The Smart POS for Restaurants
DigiPos is designed to streamline POS operations in restaurants, ensuring compliance with ZATCA’s e-invoicing regulations. DigiPos automatically generates and submits invoices to ZATCA’s Fatoora platform in real-time, eliminating the need for manual data entry. Additionally, DigiPos generates QR codes on all receipts for B2C transactions, making it easier for consumers to validate the authenticity of the invoice.
- Real-time submission of invoices to ZATCA's platform.
- Automatic QR code generation for all consumer transactions.
- Optimized for fast-paced environments like restaurants and cafes.
- Support for multiple languages, accommodating diverse customer bases.
ERPNext: Scalable ERP Solution
ERPNext is an adaptable ERP solution designed to integrate seamlessly with ZATCA’s platform, ensuring that businesses can generate ZATCA-compliant invoices without complexity.
- Offers customizable reports aligned with ZATCA’s standards to help businesses maintain compliance.
- Seamless integration with inventory and accounting systems for more efficient reporting and tax management.
- Supports bulk invoice submissions, particularly useful for businesses engaged in B2B transactions with high-volume invoicing requirements.
- Advanced financial tracking and automated tax reporting to streamline reconciliation and audit processes.
PixelPoint: Robust POS for Hospitality
PixelPoint is an advanced POS system designed for the hospitality industry, offering full ZATCA Phase 2 Integration compliances. It caters to dine-in, takeaway, and delivery operations with customizable workflows and a user-friendly interface.
- Supports dine-in, takeaway, and delivery operations while adhering to ZATCA’s real-time invoicing requirements.
- Enables seamless integration with ZATCA for real-time validation and submission of invoices.
- Customizable workflows that support complex order handling, such as split bills or service charges.
- Fast and intuitive interface designed for high-volume transactions in the hospitality industry.


